What is IEEE-1394?
IEEE-1394 is a high-speed digital serial interface that has data transfer speeds
up to 400 Mbps today. 1394 enables plug-and-play peripheral connectivity,
provides power to peripherals, supports real-time (isochronous) data transfers
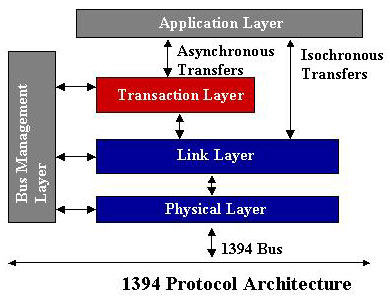
and digital transport content protection. The 1394 architecture comprises of
three layers -- physical, link, and transaction- corresponding to the lowest
three layers of the International Standardís Organizationís Open Systems
Interconnection (OSI) model. Unlike USB, which is a PC host-based architecture,
1394 is a peer-to-peer protocol, allowing a peripheral such as a digital camera
or camcorder to plug directly into a printer without the need for a PC host.
Typically, 1394 is used in applications requiring one or more of the following
attributes such as high data rates, isochronous capabilities, plug and play, and
peer-to-peer connectivity. 1394 has been designed into PCís, printers, hard
disk drives, scanners, adapter cards, digital cameras, digital camcorders,
printers, digital VCRís, high-definition TVís, and cable set-top boxes.
The Latest on IEEE-1394 Specifications
The current approved specification is IEEE-1394-1995.
The next specification in the final approval ballot stage is IEEE-1394a. It
supplements the IEEE-1394-1995 specification with improvements targeted to
interoperability and performance while maintaining compatibility with current
products. It also clarifies some ambiguous specifications in the original
IEEE-1394-1995 specification.
1394b Specification
Currently in development is the first draft of the IEEE-1394b specification.
Highlights of the new specification, include data rates up to 3.2 Gbps and cable
distances up to 100 meters using unshielded twisted pair (UTP) or optical fiber.
Get the IEEE 1394 Specifications
The 1394-1995 specification is only available from the IEEE. You can obtain it
through the IEEE website at www.ieee.org.
The 1394a specification is in final approval stages and will be available from
the IEEE website when it is approved.
The 1394b and 1394.1 specifications are in development and not yet publicly
available.
IEEE-1394 FAQs
- Is USB 2.0 going to replace IEEE 1394?
Those familiar with the two specifications believe the two bus standards
will complement one another. Today, 1394 is ideally suited for the higher
performance isochronous and asynchronous video/audio/data transfer
applications. In comparison, USB handles lower-speed peripheral applications
very well. For example, many PCís contain ports for both standards because
of their complementary capabilities.
- What 1394 products are available today?
1394 enabled PCís, digital cameras, digital camcorders, printers,
scanners, storage devices, network hubs, digital TVís, and digital VCRís
are currently available.
- Where can I find out more information on 1394?
The 1394 trade association has approximately 200 member companies that are
developing 1394 products. Their website contains useful information about
the 1394 technology, the membership, upcoming 1394 industry events, and how
to become a member. Member benefits include the ability to participate in
the various working groups that are formulating the next-generation 1394
specifications.1394 Trade Association: www.1394ta.org

